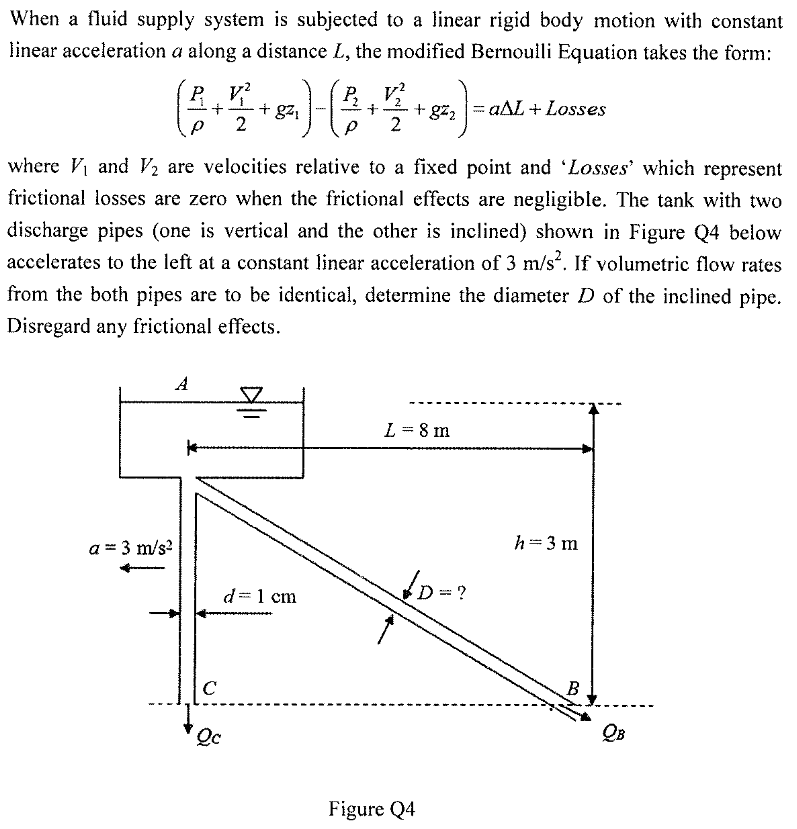
Extracted text: When a fluid supply system is subjected to a linear rigid body motion with constant linear acceleration a along a distance L, the modified Bernoulli Equation takes the form: P V? + g21 2 2 aAL+ Losses + gz2 2 ww -- where V and V2 are velocities relative to a fixed point and 'Losses' which represent frictional losses are zero when the frictional effects are negligible. The tank with two discharge pipes (one is vertical and the other is inclined) shown in Figure Q4 below accelerates to the left at a constant linear acceleration of 3 m/s. If volumetric flow rates from the both pipes are to be identical, determine the diameter D of the inclined pipe. Disregard any frictional effects. A L = 8 m h=3 m a = 3 m/s? ? d=1 cm C B Qc Figure Q4