The mode of a set of numbers is that value which occurs with the greatest frequency; that is, it is the most common value. The mode may not exist, and even if it does exist it may not be unique.
1. The set 2, 2, 5, 7, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 11, 12, and 18 has mode 9.
2. The set 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, and 16 has no mode.
3. The set 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 7, 7, and 9 has two modes, 4 and 7, and is called bimodal.
A distribution having only one mode is called unimodal.
In the case of grouped data where a frequency curve has been constructed to fit the data, the mode will be the value (or values) of X corresponding to the maximum point (or points) on the curve. This value of X is sometimes denoted by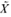
From a frequency distribution or histogram the mode can be obtained from the formula
Where L1 ¼ lower class boundary of the modal class (i.e., the class containing the mode)
?1 = excess of modal frequency over frequency of next-lower class
?2 = excess of modal frequency over frequency of next-higher class
c = size of the modal class interval