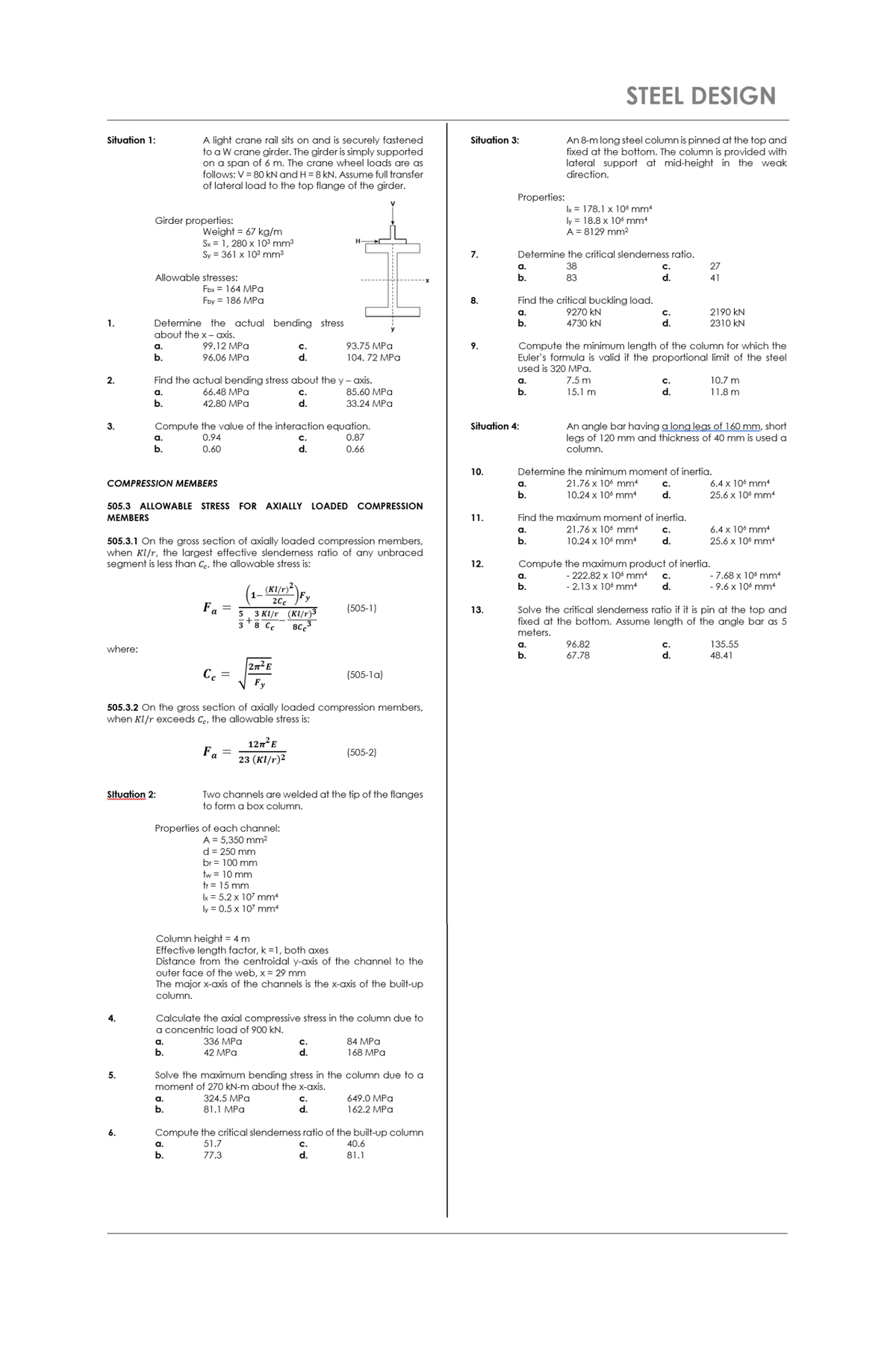
Extracted text: STEEL DESIGN Situation 1: Situation 3: A light crane rail sits on and is securely fastened to a W crane girder. The girder is simply supported on a span of 6 m. The crane wheel loads are as follows: V = 80 kN and H = 8 kN. Assume full transfer of lateral load to the top flange of the girder. An 8-m long steel column is pinned at the top and fixed at the bottom. The column is provided with lateral support at mid-height in the weak direction. Properties: Ix = 178.1 x 10 mm4 Girder properties: ly = 18.8 x 106 mm4 A = 8129 mm²2 Weight = 67 kg/m Sx = 1, 280 x 10³ mm3 Sy = 361 x 103 mm3 7. Determine the critical slenderness ratio. a. 38 c. 27 Allowable stresses: b. 83 d. 41 Fbx = 164 MPa Find the critical buckling load. 9270 kN Fby = 186 MPa 8. 2190 kN 2310 kN a. с. Determine the actual bending stress about the x- axis. 1. b. 4730 kN d. Compute the minimum length of the column for which the Euler's formula is valid if the proportional limit of the steel used is 320 MPa. a. 99.12 MPa С. 93.75 MPa 9. b. 96.06 MPa d. 104. 72 MPа 2. Find the actual bending stress about the y - axis. 7.5 m C. d. a. 10.7 m a. 66.48 MPа C. 85.60 MPa b. 15.1 m 11.8 m b. 42.80 MPa d. 33.24 MPa Compute the value of the interaction equation. 0.87 An angle bar having a long legs of 160 mm, short legs of 120 mm and thickness of 40 mm is used a column. 3. Situation 4: а. 0.94 с. b. 0.60 d. 0.66 10. Determine the minimum moment of inertia. COMPRESSION MEMBERS a. 21.76 x 106 mm4 с. 6.4 x 106 mm4 b. 10.24 x 106 mm d. 25.6 x 106 mm 505.3 ALLOWABLE STRESS FOR AXIALLY LOADED COMPRESSION MEMBERS 1. Find the maximum moment of inertia. 21.76 x 106 mm4 6.4 x 106 mm4 C. d. a. 10.24 x 106 mm 505.3.1 On the gross section of axially loaded compression members, when Kl/r, the largest effective slenderness ratio of any unbraced segment is less than Ce, the allowable stress is: b. 25.6 x 106 mm 12. Compute the maximum product of inertia. - 222.82 x 10 mm4 - 2.13 x 106 mm4 - 7.68 x 106 mm - 9.6 x 106 mm a. с. (KI/r)²' b. d. 20c Fa = (505-1) Solve the critical slenderness ratio if it is pin at the top and fixed at the bottom. Assume length of the angle bar as 5 meters. 13. 5. 3 KI/r (KI/r)3 38 Cc 80 96.82 67.78 a. 135.55 where: b. d. 48.41 2n E C. (505-1a) Fy 505.3.2 On the gross section of axially loaded compression members, when Kl/r exceeds Ce, the allowable stress is: 127²E Fa (505-2) 23 (кI/r)2 Situation 2: Two channels are welded at the tip of the flanges to form a box column. Properties of each channel: A = 5,350 mm2 d = 250 mm br = 100 mm tw = 10 mm tr = 15 mm Ix = 5.2 x 107 mm ly = 0.5 x 107 mm Column height = 4 m Effective length factor, k =1, both axes Distance from the centroidal y-axis of the channel to the outer face of the web, x = 29 mm The major x-axis of the channels is the x-axis of the built-up column. Calculate the axial compressive stress in the column due to a concentric load of 900 kN. 4. a. 336 MPа с. 84 MPa b. 42 MPа d. 168 MPа Solve the maximum bending stress in the column due to a moment of 270 kN-m about the x-axis. 5. a. 324.5 MPa с. 649.0 MPa b. 81.1 MPa d. 162.2 MPa Compute the critical slenderness ratio of the built-up column a. 51.7 c. 40.6 b. 77.3 d. 81.1