Percolation – 110 course points
The purpose of this assignment is to practice your understanding of the Union-Find data type and the 2D array data structure.
Start your assignment early!You need time to understand the assignment and to answer the many questions that will arise as you read the description and the code provided.
Refer to our ProgrammingAssignments FAQfor instructions on how to install VSCode, how to use the command line and how to submit your assignments.
Background
So far, we have learned about an abstract data type called Union Find that organizes data into disjoint sets and allow us to: (1) unify two sets, and (2)given an element of a set it finds the representative of the set. With that knowledge, together with some clever tricks, we can test if an-by-ngrid percolates.
Percolation is an abstract model for many physical systems. Given an-by-ngrid of sites, each site is open with probabilityp, the system percolates if and only if any open site in the top row in the grid is connected to any open site in the bottom row by open sites.
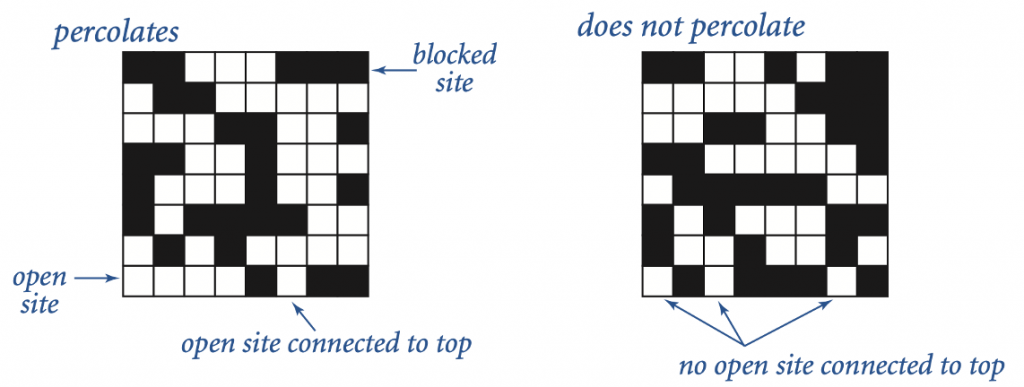
We model percolation as a dynamic-connectivity problem and use union-find to check if the system percolates.
How to model Percolation as a dynamic-connectivity problem?
- Initialize an-by-ngrid of sites, where all sites are closed/blocked.
- Initialize a weighted quick union-find object containing all the sites in the grid plus two additional sites: a virtual top and a virtual bottom.
- Open all sites.
- Check if the system percolates.
Opening all sites
- Starting at the first site (0,0), one row at a time, open each site with probabilityp.
Open site
- If site is closed, open. Otherwise, do nothing.
- If opened site is in the first row then connect to virtual top.
- If opened site is in the last row then connect to virtual bottom.
- Connect opened site to any adjacent site that is open. An adjacent site is a site to the left, right, top, or bottom of the site. (Not diagonals).
Does the system percolate?
The system percolates if virtual top site is connected to virtual bottom site.
Overview of files
You are tasked with completing 3 methods under the Percolation class:openSite,openAllSites, andpercolationCheck.
Files provided
- StdDraw.java
- Used by Percolation.java to draw the grid.
- StdRandom.java
- Used by Percolation.java to generate random numbers.
- WeightedQuickUnionFind.java
- Used by Percolation.java to store information about whichopen sitesare connected or not.
- Percolation.java
- This is the file you will update and submit. It contains the information for the grid.
Percolation.java
Instance variables
boolean[][] grid: boolean 2D array representing the grid. Each (row, col) is a site. (row, col) is true if the site is open, false if the site is closed.
int gridSize: the size of the grid.
int gridSquared: the number of sites in a grid.
WeightedQuickUnionFind wquFind: Weighted quick union-find object used to keep track of all connected/opened sites.
int virtualTop: index of a virtual top in the size and parent arrays inWeightedQuickUnionFind. Connect the virtual top to every open site in the first row of the grid.
int virtualBottom: index of a virtual bottom in the size and parent arrays in WeightedQuickUnionFind.
Methods
constructor: initializes the object’s instance variables. Do not update.
openSite(): opens a site at (row, col). If the site is already open, do nothing. You complete this method.
openAllSites(): opens all sites in the grid.Starting at the first site at index (0,0) and moving row wise through all the sites, each site is opened with probabilityp.You complete this method. UseStdRandom.uniform()to generate a random number.
percolationCheck(): returns true if the system percolates.You complete this method.
displayGrid(): displays the grid. An open site is colored blue, a closed site is colored black.
main(): for testing only, update freely.
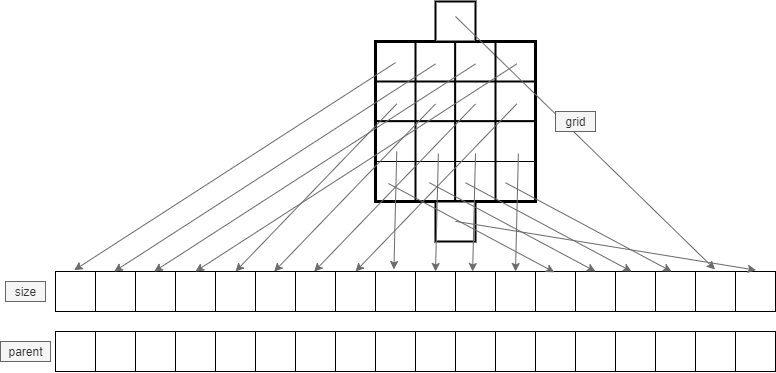
The following picture depicts the relationship of the grid sites to the size and parent arrays in the WeightedQuickUnionFind object.
- The 2D array grid is flattened into a 1D array.
- The 1D array has an additional two sites: the virtual top and bottom sites.
- The virtual top corresponds to the next to last index in size/parent array, the virtual bottom corresponds to the last index in the size/parent array.
Implementation
- You are to complete the methods openSite(), openAllSites(), and percolationCheck() in the Percolation.java file.
- YOU MAY only update the methods openSite(), openAllSites(), and percolationCheck().
- YOU MAY call displayGrid() from inside the main method only.
- DO NOT add any public methods to the percolation class.
- YOU MAY add private methods to the percolation class.
VSCode Extensions
You can install VSCode extension packs for Java. Take a look atthis tutorial. We suggest:
Importing VSCode Percolation Project
- Download percolation.zip fromAutolab Attachments.
- Open VSCode
- Import the project to a workspace throughFile>Open FolderorFile>Open Workspace
Executing and Debugging
- You can run your program through VSCode or you can use the Terminal to compile and execute. We suggest running through VSCode because it will give you the option to debug.
How to debug your code
- If you choose the Terminal:
- to compile: once inside the percolation/src directory, type:javac *.java
- to execute:java Percolation
Before submission
Collaboration policy. Read our collaboration policyhere.
Submitting the assignment.SubmitPercolation.javaseparately via the web submission system called Autolab. To do this, click theAssignmentslink from the course website; click theSubmitlink for that assignment.
Getting help
If anything is unclear, don’t hesitate to drop by office hours or post a question on Piazza. Find instructors office hours by clicking the
Staff
link from the course website. In addition to office hours we have theCAVE(Collaborative Academic Versatile Environment), a community space staffed with lab assistants which are undergraduate students further along the CS major to answer questions.