YesterdayApr 1 at 2:32pm
Manage Discussion Entry
Factorial Design
Using the article, "Influence of perceived co-worker involvement and supervisory support on job satisfaction" by Okediji et al. (2011). Job satisfaction is explored, in this case, they used the influence of what they believe to be a co-worker, that is how it was determined how satisfied they were. In the research conducted they show they believe the support that is or is not provided by the supervisor and career development shows a direct relationship between how happy an employee is. Factors like these can also influence a companies productivity, retention rate, and ability to attract new talent.
The 2x2 factorial design was used to analyze the data
150 participants (sample size) broken down into 95 males and 55 females, age rangesbetween 18-40.
Dependent and Independent variable
The independent variable would be the co-worker and supervisor and how they influenced. Co-workers could be categorized as helpful or not helpful. While the supervisor would be considered supportive or not based on the information given in the study, falling under the categorical independent variable column. They used the questionnaire as a way to obtain the data based on the prescriptions of co-workers and supervisors. The range for the co-worker was 60-120 whereas the supervisor was 35 to 70. The dependent variable being job satisfaction.
|
Helpful
|
Non-Helpful
|
Supportive
|
76.36
|
70
|
Non-Supportive
|
91.13
|
67
|
Based on the table the employee would be much more satisfied with their job in an environment of helpful, supportive team members around them. Which based on personal experiences that sound correct, which proves their hypothesis correct. How important it is to have a positive healthy working environment to build trust, which in turn brings more talented people into the mix and retains the current employees filled with training and company knowledge.
References
Cozby, P. & Bates, S. (2017).Methods in behavioral research (13th ed). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill..
Okediji, A. A., Etuk, A. S., & Nnedum, O. A. U. (2011). Influence of Perceived Co-Worker Involvement and Supervisory Support on Job Satisfaction.IFE PsychologIA,19(2), 28–42.
YesterdayApr 1 at 11:03pm
Manage Discussion Entry
Factorial Designs
Conducting research for an academic study is the primary way scholars support and persuade their premises and audiences. However, there are different approaches as to how scientists conduct research. For instance, depending on the research question, scientists can implement a factorial designed experiment that allows researchers to study several independent variables simultaneously (Cozby & Bates, 2017).Through the experiments conducted by authors Fernandez, Wood, Laforge, and Black (2011), I will demonstrate my understanding of factorial design by providing a brief summary of the methods used, identifying independent and dependent variables, and placing data into the correct cells of a factorial matrix.
Overview
Alcohol and alcohol-related problems have caused much harm to young students throughout history. Transitioning from high school to college is the typical time for students to become more accustomed to drinking alcohol regularly. Therefore, this transition period is the ideal time to induce preventive interventions on heavy episodic drinking (HED).
17–21-year-old students and their parents were selected at random to form two successive populations from a mid-sized university in the United States. Thus, the study used a 2x2 factorial design to investigate the effects of a “two-session motivational intervention” delivered to students and a “handbook-based parent intervention” administered to students and parents which included a follow-up assessment 10 and 22-months post-baseline (Fernandez, Wood, Laforge, & Black, 2011, p. 205).
Variables & Levels
IV (A):Two-session motivational intervention
IV (B):Handbook-based parent intervention
DV:Amount of heavy episodic drinking (HED) reported
Factorial Matrix
The study used a “2x2 factorial design with two dichotomous between-subjects factors, brief motivational intervention (yes, no) and parent-based intervention (yes, no)” (Fernandez, Wood, Laforge, & Black, 2011, p. 207). The data reflected a wide range of drinking behavior across subjects. At baseline, 28% of students reported abstaining from alcohol for at least the past year then decreased to 17% at the 10-month follow-up. Then, finally, 13% at the 22-month follow-up (Fernandez, Wood, Laforge, & Black, 2011).
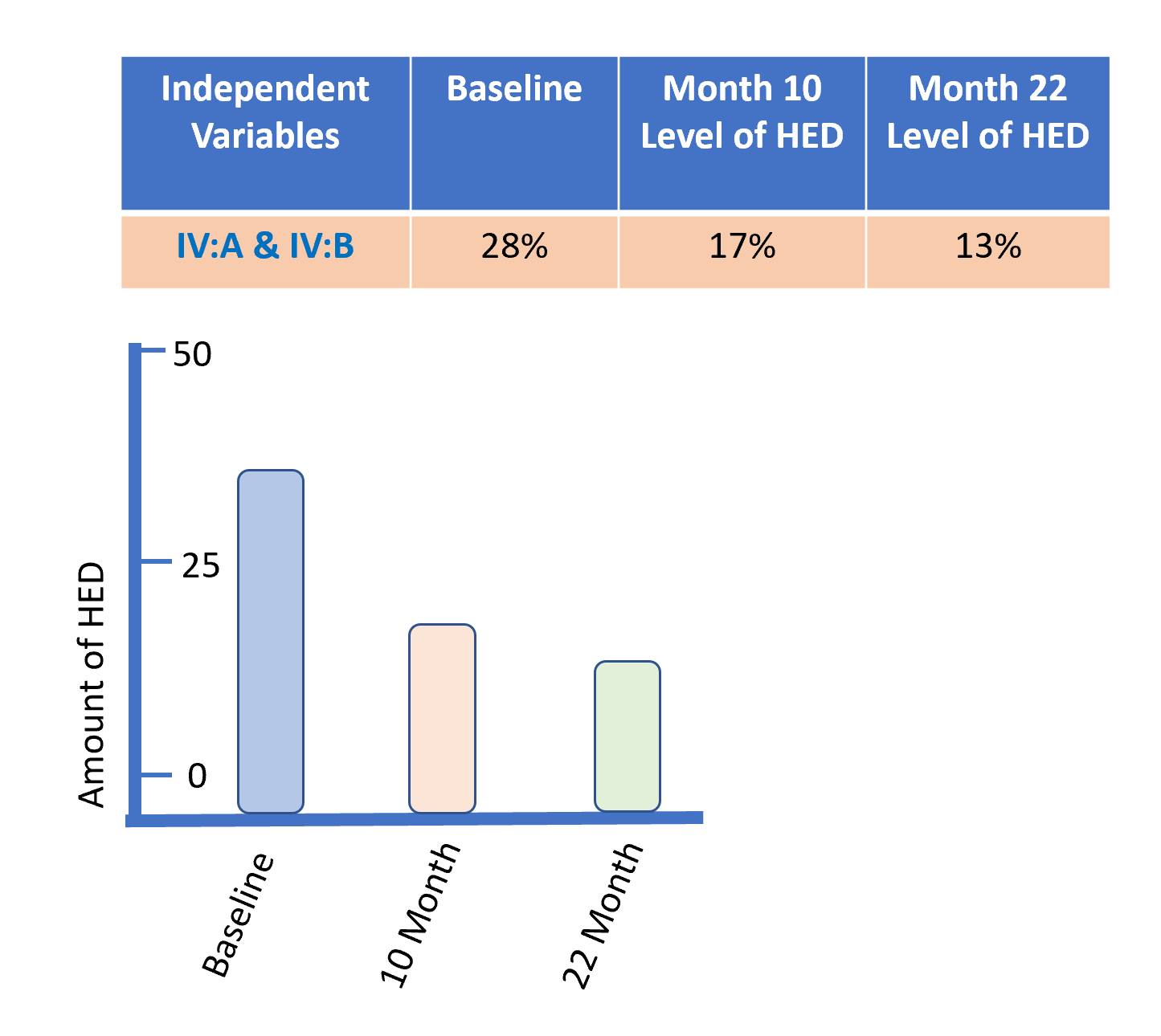
Concluding Remarks
After reviewing the results, it seems as though the “brief motivational intervention” significantly reduced the onset of HED at the 10 and 22-month mark. However, the observed effects were insignificant. Furthermore, it appears that the parent-based intervention did not reduce the onset of HED by much.
References
Cozby, P. & Bates, S. (2017).Methods in behavioral research (13th ed). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Fernandez, A. C., Wood, M. D., Laforge, R., & Black, J. T. (2011). Randomized trials of alcohol-use interventions with college students and their parents: lessons from the Transitions Project...[corrected] [published erratum appears in CLIN TRIALS 2011 Jun; 8(3):355]. Clinical Trials, 8(2), 205–213. https://doi-org.proxy-library.ashford.edu/10.1177/1740774510396387