Let f : D →
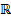
be continuous. For each of the following, prove or give a counterexample.
(a) If D is open, then f (D) is open.
(b) If D is closed, then f (D) is closed.
(c) If D is not open, then f (D) is not open.
(d) If D is not closed, then f (D) is not closed.
(e) If D is not compact, then f (D) is not compact.
(f) If D is unbounded, then f (D) is unbounded.
(g) If D is finite, then f (D) is finite.
(h) If D is infinite, then f (D) is infinite.
(i) If D is an interval, then f (D) is an interval.
(j) If D is an interval that is not open, then f (D) is an interval that is not open.