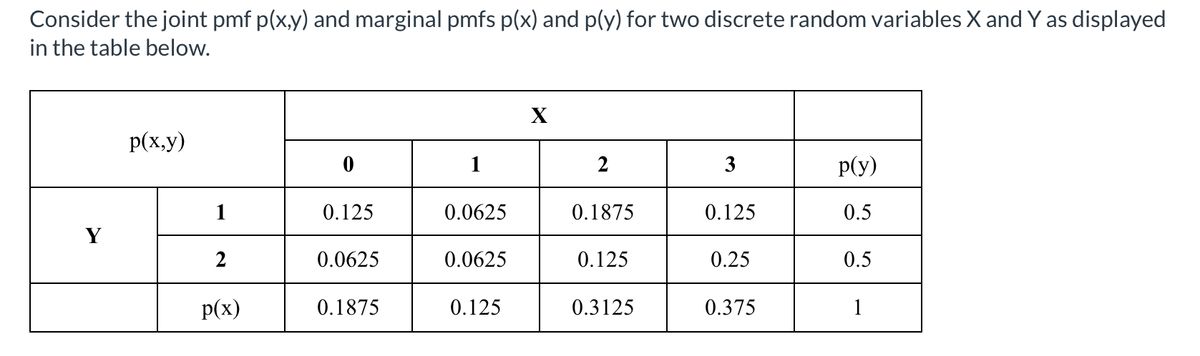
Extracted text: Consider the joint pmf p(x,y) and marginal pmfs p(x) and p(y) for two discrete random variables X and Y as displayed in the table below. X p(x,y) 1 2 3 p(y) 1 0.125 0.0625 0.1875 0.125 0.5 Y 2 0.0625 0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.5 p(x) 0.1875 0.125 0.3125 0.375 1

Extracted text: Are X and Y independent? No, p(x,y) # p(x)p(y) for x = 1, 3 and y O Yes, p(x,y) = p(x)p(y) for x = 1 and y No, p(x,y) + p(x)p(y) for x = 0, 2, 3 and y No, p(x,y) + p(x)p(y) for x = 0, 1, 2, 3 and y No, p(x,y) = p(x)p(y) for x = 0, 1 and y O No, p(x,y) # p(x)p(y) for all pairs of x and y O Yes, p(x.y) = p(x)p(y) for all pairs of x and y O O O